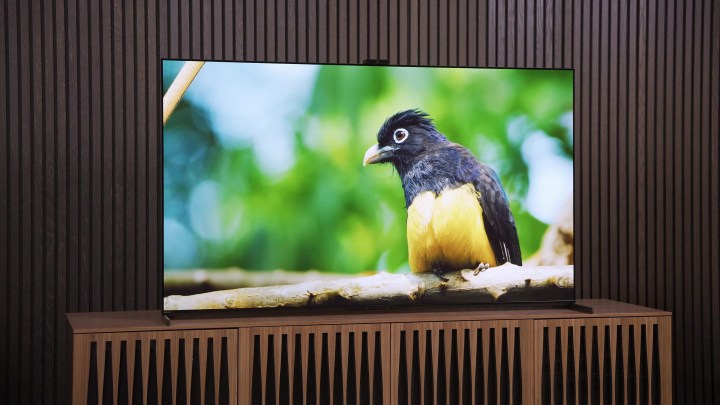
Looking for a new TV? Then there’s no doubt you’re considering and OLED TV. The class-leading television technology, which stands for Organic Light Emitting Diode, has captured the imaginations of home entertainment enthusiasts worldwide for its stunning picture quality, (nearly) unrivaled black levels, and vibrant colors.
But what is OLED TV? What makes it better (or worse) than other TV technologies out there, such as QLED, mini-LED, or QD-OLED? In our OLED explainer, we’ll investigate what OLED TV is, how it works, who makes OLED TVs, and why it might be the right choice for your next television purchase.
Understanding OLED technology
OLED TVs utilize organic compounds in their individual pixels that emit their own light (known as “self-emissive”) when an electric current is passed through them. Traditional LED, QLED, or LCD TVs, in contrast, require a backlight to illuminate their pixels on the screen. OLED’s ability to control the brightness of individual pixels leads to the superior picture quality OLEDs are known for. We get into that a bot more next.
Key benefits of OLED TVs
There are important benefits to OLED TVs and why they have become trendy.
Inky blacks and deep contrast: Since each pixel in an OLED TV produces its own light, each pixel can also be turned off completely, hence making them totally black, allowing for unrivalled contrast. LEDs and LCD TVs cannot do this, instead only being able to dim their backlights. This is the cornerstone of OLED technology, which helps deliver an incredibly lifelike viewing experience and vibrant, accurate colors.
Wide viewing angles: OLED screens’ self-emitting nature ensures that colors remain accurate and consistent, even when viewed from extreme angles. This is a massive advantage for those with expansive seating arrangements in their living rooms.
Thin and flexible designs: Without the need for backlight layers, OLED panels can be made incredibly thin, allowing for sleek TV designs that can even be flexible or curved.
Excellent response time: OLED TVs boast speedy response times, virtually eliminating motion blur. This feature particularly appeals to sports fans and gamers who crave seamless action without delay.
Why choose an OLED TV?

Deciding to invest in an OLED TV prioritizes picture quality and performance. OLEDs offer unparalleled black levels. If this is a key feature you’re looking for, OLED can rarely be beat by most LED TVs, especially if you do most of your viewing in a dark room. But that’s not to say that OLED TVs can’t also get plenty bright — they most definitely can, making an OLED TV an excellent all-rounder, whether you’re watching movies, TV shows, or sports.
Gamers are also a prime demographic for choosing an OLED, with some of the best refresh rates on the market, like the 2024 LG G4 OLED that boasts support for up to 4K/120Hz inputs and a response time of 0.1 milliseconds, making it excellent for console and PC gamers. If lag-free gaming is your jam, an OLED might be your best bet.
Furthermore, for those concerned with aesthetics, OLED TVs’ super-slim design makes them a visually appealing addition to any home entertainment setup. As for sustainability, OLED displays are generally more energy-efficient than their LCD equivalents because they don’t have a permanent backlight layer.
Considerations before buying
Despite the many advantages, there are some considerations one should take into account before purchasing an OLED TV:
Price: OLED TVs are still more expensive than LED/LCD models. However, as the technology becomes more widespread, costs have gradually decreased.
Screen burn-in: Although less of an issue with newer models, OLED TVs have been known for the potential of static images leading to screen burn-in. This can occur when a persistent part of an image, like a network logo or a game HUD, remains onscreen for extended periods without change. Most regular viewers don’t have to worry about this though.
Brightness levels: While OLEDs are unparalleled for deep blacks, they might not be as bright as some LED TVs. This can be noticeable in very bright viewing environments, like rooms with a lot of ambient light or windows during daytime hours.
Size considerations
OLED TV panels follow a manufacturing process different from that of other televisions. As they get bigger, the cost of OLED panels rises sharply. In the 50- to 65-inch size range, OLED TVs are very competitive with LED and QLED TVs in terms of price. But as you head into 70- to 98-inch territory, OLED pricing can feel more expensive than LED/QLED. For example, the 83-inch LG G4 OLED retails for $5,800 while its largest 97-inch model peaks out at $20,000.
The role of LG Display
In case you didn’t know, LG Display is the panel-manufacturing arm of LG Electronics. Its OLED panels are renowned for their exceptional picture quality, vibrant colors, and deep blacks — all the OLED traits we’ve already discussed. But LG Display doesn’t just provide OLED panels to LG TVs; the market leader also supplies its panels to several of its competitors for their OLED TVs, including Sony, Samsung, Panasonic, and others. As a result, customers can expect consistent visual performance across different brands, as they all rely on the same cutting-edge display technology.
This level of quality is made possible by LG Display’s position as a leading producer of large-size OLED panels, underscoring the reliability and excellence associated with OLED technology in the market. Not surprisingly, LG dominates our list of the best OLED TVs and best TVs overall.
What about Samsung and other manufacturers?

Samsung initially focused on AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) technology for its smartphones and tablets because of its vibrant colors, high contrast ratios, and energy efficiency. The company’s commitment to AMOLED technology was evident in popular devices such as the Galaxy series.
In 2013, Samsung made its first venture into the OLED TV market (the Samsung KN55S9C OLED TV), showcasing its expertise in display technology beyond mobile devices. However, Samsung later shifted its focus to QLED (quantum dot LED) technology, which offered improvements in brightness and a wider color gamut. This strategic move differentiated Samsung from its competitor, LG, which continued to prioritize and advance its OLED offerings for TVs and displays.
Despite the shift toward QLED, Samsung has yet to retreat from the OLED landscape entirely and continues to innovate in display technologies, specifically with its “best of both worlds” OLED/QLED hybrid technology, QD-OLED. We have a full explainer on QD-OLED as well, but the “Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diodes” tech combines a layer of quantum dots built into a self-emissive OLED screen for a combination of brilliant brightness and color.
Sony
Sony is another heavyweight in the OLED TV market. The brand has consistently been synonymous with high-quality electronics; its venture into OLED TVs is no exception. Sony’s TVs blend the company’s proprietary technologies with the OLED panels sourced from LG Display (such as the A80J OLED) to enhance the audio-visual experience. Additionally, Sony’s Acoustic Surface Audio technology, in particular, turns the entire screen into a speaker, providing an immersive sound experience that complements the stunning visuals of OLED.
Sony also uses LG Display’s OLED panel in its new Bravia 8 OLED line, but its higher-end models, like the Bravia A95L, use Samsung’s QD-OLED panel. Keeping up? It’s safe to say that all consumer OLED TVs in the U.S. are either LG for OLED or Samsung for QD-OLED, and only Samsung and Sony have QD-OLED TVs.
Panasonic
Panasonic has a reputation for producing some of the most critically acclaimed OLED TVs in the market, especially for their accuracy in color reproduction. This makes them a favorite among professionals in the filmmaking industry. But until recently, the famed company had taken a long break from selling its TVs in the U.S. Panasonic also utilizes panels from LG Display (and the new TVs it will sell in the U.S. will, too) and integrates its own image processing techniques to further refine the picture quality.
The future of OLED TV production
As manufacturers continue to invest and innovate in OLED technology, future advancements are expected to enhance performance, reduce costs, and provide even more flexible and varied display options. The potential for OLED applications extends beyond televisions, promising exciting developments in smartphones, tablets, and wearables.
OLED TVs are at the pinnacle of current television technology, offering exceptional picture quality that is especially noticeable in dark environments. They are a fantastic choice for those who value the cinematic quality of their viewing experiences and are willing to invest in top-tier technology.
As the technology matures, we can anticipate wider adoption, making OLED an even more attractive option for the average consumer.
Whether you’re a cinephile seeking out the most lifelike picture possible or a gamer needing the quickest response time, an OLED TV might be the perfect centerpiece for your digital entertainment and a glimpse into the future of display technology.